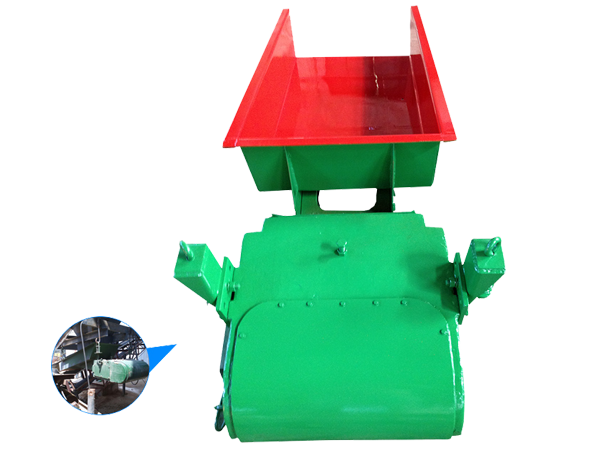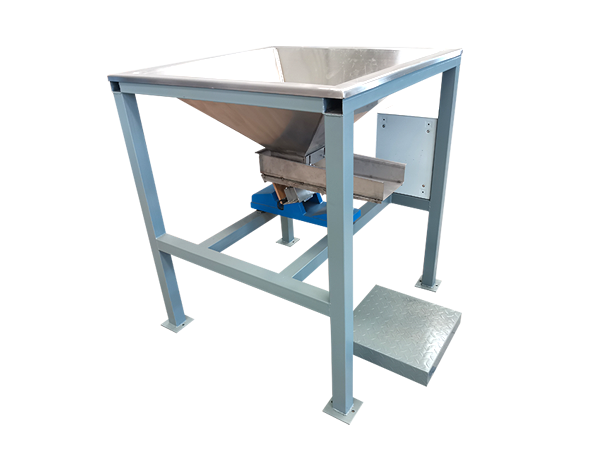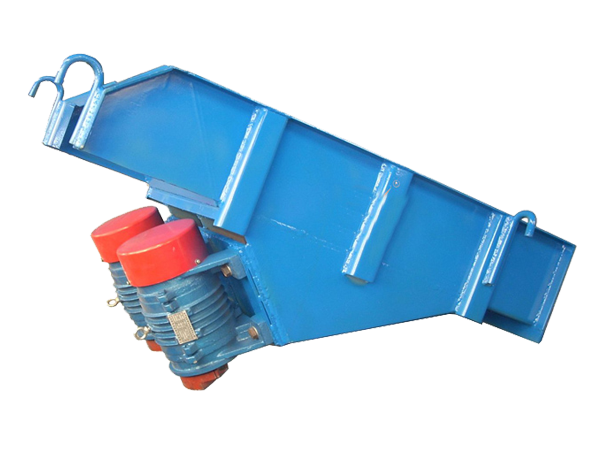
Vibrating Feeder
Used to feed powder, granules, bulk raw materials or finished products into crushers, hoppers, chutes or final containers.
Type: Motor/Electromagnetic
Feeding particle size: 120~360mm
Output: 40~600 tons/hour
Frequency: 50-60 Hz (electromagnetic) or 50-100 Hz or even higher (motor)
Application: Suitable for a variety of materials, from fine powder to large bulk materials, commonly used to feed materials into crushers, screens and other processing equipment in various industries such as mining, construction, chemical and food processing.
Introduction of Vibrating Feeder
Vibrating feeder is a type of equipment used to transport and feed bulk materials into a production process. It utilizes vibration to move materials along a designated path, typically into hoppers, chutes, or other equipment.
The device use electromagnetic or electromechanical drives to produce vibrations. This motion helps to move materials smoothly and consistently, and the feed rate can usually be adjusted by varying the amplitude and frequency of the vibrations to precisely control the flow of material.
Types of Vibrating Feeder
There are primarily two types of vibrating feeders:

Electromagnetic Vibrating Feeders: They use electromagnetic coils to generate vibrations. The vibration frequency and amplitude are precisely controlled. They are very suitable for handling delicate materials and are often used in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
Mechanical Vibrating Feeders: They use eccentric motors to generate vibrations. They are used to separate and screen materials before they enter the primary crusher. They are designed to handle large pieces of material with high impact loads. They are more rugged than electromagnetic feeders and are very suitable for heavy-duty applications. They are often used in the mining and construction industries.
Motor vibrating feeder and electromagnetic vibrating feeder are two common vibrating feeding equipments, they have some differences in working principle, structure, performance and so on.
Difference Mechanical Vibrating Feeder Electromagnetic Vibrating Feeder
| Working principle | Motor eccentric force | Electromagnetic force |
| Structure | Simple | Complex |
| Vibration frequency | Fixed | Adjustable |
| Vibration amplitude | Large | Small |
| Control accuracy | Low | High |
| Maintenance cost | Low | High |
| Scope of application | Large flow, coarse-grained materials | Fine materials, high-precision control |
Tips: If the material flow is large, the particle size is coarse, and the control accuracy requirement is not high, you can choose a motor vibrating feeder; if the material is fine and the flow control accuracy requirement is high, you can choose an electromagnetic vibrating feeder.
Technical parameters
| Model | Width(mm) | Power(KW) | Angle(°) | Capacity(T/H) | Weight(kg) |
| DZC30250 | 300 | 0.75 | 0~5 | 15-30 | 325 |
| DZC30300 | 300 | 0.75 | 15-25 | 390 | |
| DZC50350 | 500 | 1.5 | 30-50 | 515 | |
| DZC50400 | 500 | 1.5 | 30-40 | 590 | |
| DZC50450 | 500 | 1.5 | 25-30 | 665 | |
| DZC50500 | 500 | 3 | 50-80 | 820 | |
| DZC50550 | 500 | 3 | 40-70 | 900 | |
| DZC50600 | 500 | 3 | 30-60 | 980 | |
| DZC50650 | 500 | 3 | 30-50 | 1060 | |
| DZC50700 | 500 | 3 | 30-40 | 1140 | |
| DZC50750 | 500 | 3 | 20-30 | 1220 | |
| DZC70800 | 700 | 4.4 | 80-140 | 1800 | |
| DZC70850 | 700 | 4.4 | 80-130 | 1920 | |
| DZC70900 | 700 | 4.4 | 80-120 | 2040 | |
| DZC70950 | 700 | 4.4 | 70-110 | 2160 | |
| DZC701000 | 700 | 4.4 | 60-100 | 2280 |
Special design
| Type | Image | Application |
| Basic Vibrating Feeders |
 |
Feeding materials without special requirements |
| Hanging Vibrating Feeders |
 |
Suitable for occasions where space is limited or flexible layout is required, and it is usually suspended from the structure to work. |
| Enclosed Vibrating Feeders |
 |
Feeding fragile particles, large dust and volatile materials |
| Open Vibrating Feeders |
 |
Used for coal preparation, and can also be used for feeding screening equipment |
| Heightened Vibrating Feeders |
 |
It is mainly used for feeding bulk materials and is suitable for applications at high places or with large inclination angles. |
| Vibrating Tube Feeders |
 |
Used for conveying particles or powdered materials over a long distance |
Features and Benefits

Utilizing the self-synchronizing principle of a vibrating motor, this feeder offers smooth operation, quick startup, smooth shutdown, low noise, and low energy consumption. Suitable for handling bulk, granular, or powdered materials with feed sizes ranging from 120 to 360 mm, it can achieve a daily output of 40 to 600 tons. The material continuously bounces along a parabolic trajectory, minimizing wear on the feed chute. The excitation force is adjustable, allowing for easy and stable flow control. The enclosed structure prevents dust contamination. This series of motor vibrating feeders is not suitable for applications requiring explosion-proof performance.
Videos
Structure of Vibrating Feeder
The structure of a vibrating feeder usually consists of the following main parts:
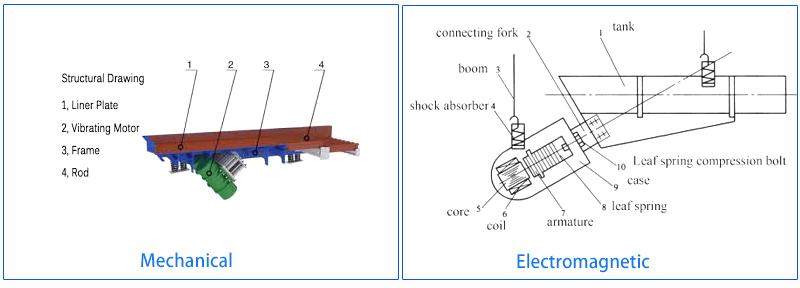
Chutes are used to carry and convey materials. They are typically made of wear-resistant materials and can be flat or V-shaped.
There are two types of vibrating devices: electromagnetic vibrators, which use electromagnetic force to generate vibration and are suitable for small and medium-sized feeders; and electric vibrators, which use an electric motor to drive an eccentric wheel to generate vibration and are suitable for most applications.
The support frame, typically made of steel, provides stable support and prevents displacement during vibration. Springs are used to isolate vibrations, reduce impact on the support structure, and ensure equipment stability.
The control system adjusts the vibration frequency and amplitude to achieve precise control of material flow.
Vibrating Feeder Working Principle
The workflow of a vibrating feeder usually includes the following main steps:
Material preparation: The material is conveyed from the storage device (such as a silo or bucket) to the feed port of the vibrating feeder.
Vibration drive: The vibrating feeder generates vibrations through electromagnetic or electric vibrators. This vibration causes the material to move in a certain direction in the trough of the feeder.
Material flow: Due to the effect of vibration, the material is pushed in the feed trough to form a uniform flow. The frequency and amplitude of the vibration can be adjusted to control the flow rate of the material.
Quantitative feeding: The vibrating feeder can achieve quantitative feeding of materials by adjusting the intensity and frequency of vibration to ensure a stable material supply to downstream equipment.
Application
Vibrating feeders have a wide range of applications in the industrial and manufacturing fields. The following are some common applications of vibrating feeders:

Mining and mineral processing: Used to transport raw ore from storage bins to crushers, mills or screening equipment.
Building material production: Used to transport raw materials such as stone, sand, cement to equipment such as concrete mixing plants or bricklaying machines.
Food processing and packaging: Used to transport food raw materials such as grains, powders, and sugar to mixers, packaging machines or other processing equipment.
Chemical production: Used to transport chemical raw materials and granular products to reactors, dryers or mixing equipment.
Pharmaceutical industry: Transport drug raw materials to pharmaceutical production equipment such as mixers, packaging machines or tablet presses.
Agricultural field: Transport granular materials such as feed and fertilizer to livestock and poultry breeding equipment.
Electronic equipment production: It can be used to transport small parts such as electronic components and cables to the production line for assembly.
Solutions by Industry

How to Choose Vibrating Feeder?

Material characteristics: the particle size directly affects the structural design and vibration frequency of the vibrating feeder. The material density affects the conveying capacity and driving power of the feeder. Materials with too high humidity may stick to the trough, affecting the smooth feeding. Materials with strong abrasiveness have higher requirements for the material of the trough. Materials that are easily broken need to choose a feeder with a smaller vibration amplitude.
Conveying capacity: According to the needs of the production line, determine the amount of material that needs to be conveyed per hour. Excessive or too small conveying capacity will affect production efficiency.
Feeding accuracy: For production processes with higher requirements, it is necessary to select a vibrating feeder with high feeding accuracy. Feeding accuracy is related to factors such as vibration frequency, amplitude, and trough structure.
Working environment: High or low temperature environments may affect the performance of the equipment. High humidity environments may cause equipment corrosion. Dust environments require equipment to have good sealing.
Installation space: Determine the installation size and location of the vibrating feeder based on the actual situation on site.