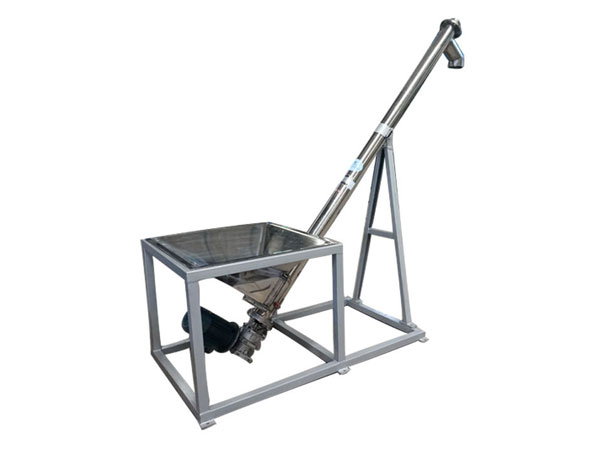

Angled Screw Conveyor
It is a conveyor system used to transport bulk materials in an inclined manner. It can convey materials such as powders, granules and bulk solids in an inclined upward manner.
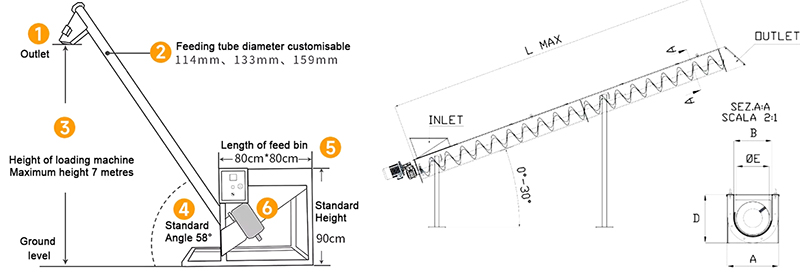
Angle: 0-60°
Conveying length: 3-20 meters
Conveying height: ≤5 meters
Capacity: 0.1-100m³/h
Application:Used for inclined conveying of bulk materials in feed, chemical, food processing, grain processing, grain storage, various additives, construction engineering and other industries.
Product Introduction of Angled Screw Conveyor
Angled screw conveyor is a conveying system that uses spiral blades to transport bulk materials in an inclined manner. This design allows for efficient material handling in applications that require elevation, with an inclination angle generally within 60 degrees, and is used to evenly feed non-sticky powdered, granular and small-particle materials from storage equipment such as silos to receiving equipment such as silos, silos, tanks or other processing equipment.
Angled screw conveyor can be customized according to user requirements with different diameters, different lengths, and different inclinations, and can be equipped with a speed-adjusting motor to continuously adjust the speed to achieve the purpose of quantitative feeding.
Maximum angle of angled screw conveyor

Inclined screw conveyors generally operate at a certain inclination, with a maximum inclination of up to 60 degrees. As the slope increases, the efficiency will decrease due to gravity, so the motor power also needs to be increased, and the efficiency is also affected by the groove type and pitch. Our experts recommend using a smaller slope as much as possible to achieve maximum efficiency.
Small angle inclination (less than 20°): The conveying distance is moderate, taking into account horizontal conveying and a small amount of lifting, suitable for short-distance conveying and slightly lifting materials, such as conveying materials from one device to another.
Medium angle inclination (20°~45°): The conveying distance is moderate and the lifting capacity is strong. It is suitable for occasions where the conveying distance and lifting height requirements are not high, such as conveying materials from the ground to the equipment feed port.
Large angle inclination (45°~60°): The lifting capacity is strong, but the conveying distance is short, and the wear on the equipment is greater. It is suitable for large-angle material lifting, such as lifting materials from a pit to a high-level storage silo.
It's important to note that the maximum angle achievable depends on factors like:
Material properties: The density, flowability, and particle size of the material.
Screw design: The pitch, diameter, and flight design of the screw.
Motor power: The power of the motor driving the screw.
Working principle of angled screw conveyor
Material Intake: The material to be conveyed enters the conveyor through an inlet hopper or chute. Gravity or an additional feeding mechanism can be used to introduce the material into the conveyor system.
Screw Rotation: The screw, also known as an auger, is driven by a motor and rotates inside the conveyor tube or trough. The rotation of the screw creates a continuous helical or spiral motion.
Material Transportation: As the screw rotates, the helical flights or paddles of the screw push the material forward along the length of the conveyor. The material is trapped between the flights and the inner surface of the tube, causing it to move in the direction of the screw's rotation.
Inclined Movement: In an angled screw conveyor, the conveyor tube or trough is set at an inclined angle, allowing the material to be transported vertically or at an inclined angle. The angle of inclination determines the steepness of the conveyor.
Discharge: As the material reaches the top or discharge end of the conveyor, it is typically discharged into a receiving hopper, chute, or another conveyor system for further processing or storage.
Features of angled screw conveyor
Inclined Transport-- Angled screw conveyors are used when there is a need to move materials vertically or at an inclined angle. The angle of inclination can vary depending on the application and the specific requirements of the material being transported.
Space Efficiency--Angled screw conveyors are space-efficient and can be used to transport materials in areas where space is limited, such as in processing plants or production facilities.
Versatility-- They can handle a wide range of materials, including powders, granules, flakes, and other bulk solids. The design can be customized to suit the specific characteristics of the material being conveyed.
Continuous Operation-- Screw conveyors are known for their continuous operation, allowing for a steady flow of materials without the need for frequent starts and stops.
Video
Difference between angled screw conveyor and horizontal screw conveyor
The main difference between an angled screw conveyor and a horizontal screw conveyor lies in the orientation and purpose of their operation. Here's a brief step-by-step explanation highlighting the differences:
| Difference | Angled Screw Conveyor | Horizontal Screw Conveyor |
|
|
|
|
| Orientation | The delivery pipe or trough remains parallel to the ground | The tubes or troughs are set at a tilted angle, allowing vertical or tilted movement of the material. |
| Material Transport | Convey materials in the horizontal direction. The screw pushes the material forward along the trough, from the inlet to the outlet | Used to handle materials that require vertical or inclined conveying. The angle of inclination determines the steepness of the conveyor and the direction of material movement |
| Application | Typically used in horizontal material transfer or conveying operations, such as moving bulk materials from one point in a production line to another or transferring materials into storage containers. They are suitable for applications where the material does not require significant elevation changes | when materials need to be moved vertically or at an oblique angle, angled screw conveyors are used. They are typically used in applications that require materials to be lifted to a higher level or transported along slopes |
| Design Considerations | While appropriate design considerations are still required, more attention is being paid to factors such as material flow, capacity requirements, and equipment size | The angle of inclination needs to be considered, which affects the flow characteristics of the material, the potential for material slippage or backflow, and power requirements |
Technical Parameters
| Model |
Spiral diameter (mm) |
Screw-pitch (mm) |
Speed (r/min) |
Capacity (m³/h) |
| LS-100 | 100 | 100 | 140 | 2.2 |
| LS-160 | 160 | 160 | 112 | 7 |
| LS-200 | 200 | 200 | 100 | 13 |
| LS-250 | 250 | 250 | 90 | 22 |
| LS-315 | 315 | 315 | 80 | 31 |
| LS-100 | 100 | 355 | 71 | 56 |
| LS-500 | 500 | 400 | 63 | 98 |
| LS-630 | 630 | 450 | 50 | 140 |
| LS-800 | 800 | 500 | 40 | 300 |
| LS-1000 | 1000 | 560 | 32 | 280 |
| LS-1250 | 1250 | 630 | 25 | 380 |
Structural of angled screw conveyor
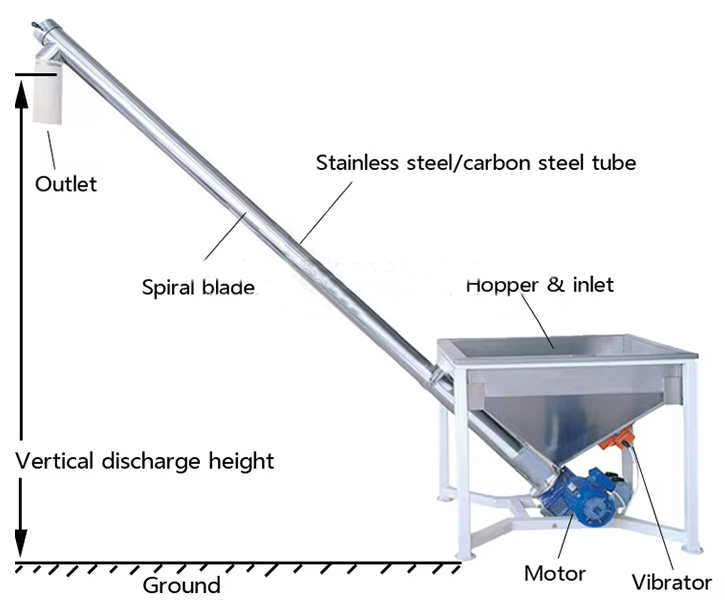
Screw Design: The screw or auger inside the conveyor is typically designed with a helical shape and a variable pitch. This design allows for efficient movement of the materials while providing adequate space between the flights to prevent material blockage or jamming.
Trough Design: Angled screw conveyors can have different trough designs, such as U-shaped or tubular, depending on the specific application and material characteristics. The trough is designed to contain and guide the materials along the inclined path.
Drive and Control: These conveyors are typically driven by an electric motor and can be equipped with speed controls to adjust the conveying rate. The speed and power requirements are determined based on the material properties, conveyor length, and angle of inclination.
Angled screw conveyor design calculation
Design and manufacturing considerations for angled screw conveyors:
Inclination from 10 degrees: Efficiency losses are minimal. Groove "U" type and standard pitch are adequate for this application. Minimal losses can be overcome by increasing speed and outside diameter or reducing pitch.
Inclination from 10 to 20 degrees: Efficiency losses range from 10% to 40%. Also, they can be overcome by increasing speed and outside diameter. Additional power is required to compensate for gravity factors.
Inclination from 20 to 30 degrees: Efficiency losses range from 10% to 70%. Tubular grooves and reduced pitch (1/2 or 2/3) are recommended for this application.
Inclination from 30 to 45 degrees: Efficiency losses range from 30% to 90%. Tubular grooves and reduced pitch (1/2 or 2/3) and larger outside diameters are recommended. Higher speed (rpm) and power are required to compensate for gravity factors.
Angled screw conveyor supporting equipment

Angled screw conveyor is a commonly used material conveying equipment. It is often used in conjunction with other equipment in the production line to achieve various processes such as material conveying, mixing, screening, and crushing.
1. With mixer: The materials to be mixed are continuously and evenly fed into the mixer to ensure the mixing effect. Small angles are suitable for mixing materials with good fluidity, and large angles are suitable for mixing materials with poor fluidity. They can accelerate the flow of materials in the mixer and improve the mixing efficiency.
2. With vibrating screen: The screened materials (materials with larger particle size) are conveyed to the designated location, or the vibrating screened materials (materials with smaller particle size) are conveyed to the next process. Small angles can reduce the impact of materials on the screen and extend the service life of the screen. Large angles can accelerate the flow of materials and improve screening efficiency.
3. With packaging machine: The processed materials are quantitatively conveyed to the packaging machine to provide a continuous and stable material supply for the packaging machine. Small angles can ensure that the materials enter the packaging machine at a relatively stable speed, reduce packaging errors, and large angles can speed up the material conveying speed and improve packaging efficiency.
4. Grinding machine: The materials to be ground are continuously conveyed to the grinding machine. A small angle can ensure that the materials enter the grinding machine evenly and improve the grinding efficiency. A large angle can accelerate the flow of materials, but it may cause excessive impact force during the grinding process, affecting product quality.
Application of angled screw conveyor
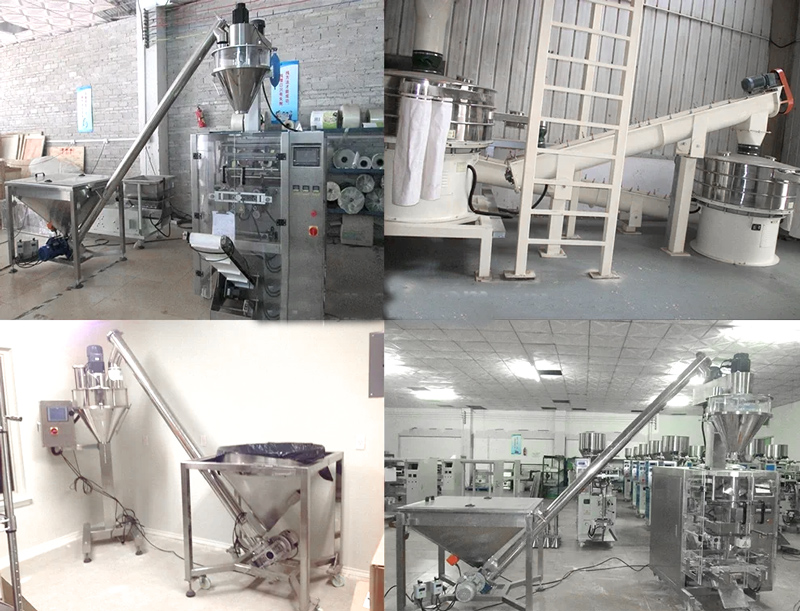

Food Processing: Angled screw conveyors are commonly used in the food industry for conveying ingredients, powders, grains, and other food products.
Agriculture: They are utilized in agricultural settings for handling seeds, grains, fertilizers, and other agricultural materials.
Mining and Construction: In mining and construction industries, angled screw conveyors are used to transport bulk materials such as ores, aggregates, and construction materials.
Chemical Processing: These conveyors play a crucial role in chemical processing plants for handling various chemicals, powders, and granular materials.
Solutions by Industry
-

Cement Factory
Use an angled screw conveyor to transport cement from the ground to an elevated storage warehouse. The inclination angle of the screw conveyor is precisely designed to lift the cement and ensure smooth flow without clogging.
-

Flour Production Line
Use an angled screw conveyor to transport flour from one production process to the next. The horizontal conveyor can efficiently move the flour to the required location, ensuring the continuity of the production line and the smooth flow of the process.
-

Plastic Pellet Recycling
Use an angled screw conveyor to transport recycled plastic pellets from the ground or lower areas to higher storage equipment or production lines. The design of the screw conveyor allows for efficient vertical lifting of plastic pellets, ensuring efficient material handling and storage.



